One of the things I try to avoid when writing this newsletter is getting too far over my skis on any particular subject. Bold predictions or declarations of victory might produce clicks at the ol’ take factory, but they can quickly prove foolish and do more harm than good in the longer term. For these and other reasons, I’ve hesitated to talk too much about China’s very rough 2023.
But the year’s almost over, the data are piling up, and … almost nobody in Washington seems to notice (at least not publicly).
Indeed, if you were to pick up a newspaper (just go with it) and turn to the politics section, you’d think that China was an unstoppable economic juggernaut destined to dominate the world at the expense of a fading United States and other Western democracies. Just yesterday, in fact, the House Select Committee on the Strategic Competition between the United States and the Chinese Communist Party released a big report decrying the CCP’s “multidecade campaign of economic aggression against the United States and its allies”—one that used an “intricate web of industrial policies” and other state planning to “achieve dominance in global markets” and “increase U.S. dependency on PRC imports”—and thus recommending a broad array of new U.S. trade/investment restrictions and subsidies (along with some decent stuff, too) to respond to this urgent economic threat.
Meanwhile, in that same (hypothetical!) newspaper’s business section, you’d see a much, much different China—one that’s struggling economically, thanks in no small part to many of the very same economic policies the Select Committee is freaking out about. Maybe someone could let them know?
China’s Economy Is in Rough Shape—Thanks in No Small Part to Chinese Government Policy
Back in late 2022, the general consensus was that the Chinese economy would surge in 2023 following the Chinese government’s sudden abandonment of its disastrous “Zero COVID” policy. For the first couple months at least, the consensus appeared to be correct: Growth, consumption, investment, and other metrics surged as China’s economy reopened and things returned to (sorta) normal. That rally proved to be short-lived, however, and signs of economic trouble—both short-term and long—have emerged almost everywhere you look.
And it’s increasingly clear that Chinese government policies warrant much of the blame.
The biggest and most obvious problem lies in China’s property sector, which has long been distorted by government policy and has struggled mightily since the high-profile collapse of behemoth developer Evergrande. According to investment bank Barclays, the Financial Times reports, “More than half of China’s top developers followed Evergrande into default after Beijing moved in 2020 to restrict new borrowing, unravelling a funding model that was built on dollar-denominated high-yield debt and bankrolled by local government financing vehicles.” As the following chart shows, dozens Chinese property firms (right Y axis)—with more than $140 billion in outstanding dollar-denominated debt (left Y axis)—have now defaulted:
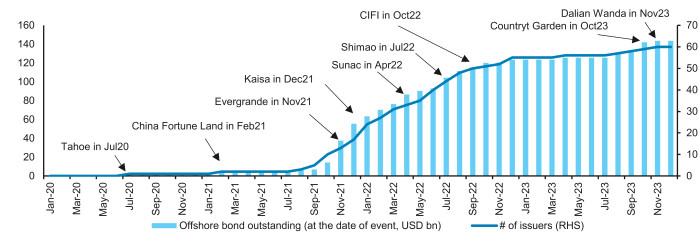
Meanwhile, many provinces in China are struggling under the weight of reckless debt—both public and hidden—accumulated during China’s boom years. The IMF estimates that “off-balance-sheet government debt” ranges somewhere between $7 trillion and $11 trillion—thanks in large part to so-called “local-government financing vehicles” (LGFVs) that borrowed gobs of money to build infrastructure or fund other local projects and companies at central planners’ prodding.
“No one knows what the actual total is,” the Wall Street Journal adds, “but it has become abundantly clear over the past year that local governments’ debt levels have become unsustainable,” with as much as $800 billion now at a “high risk” of default. China’s Finance Ministry, to its credit, told local governments to “borrow more responsibly” in the future. However, because those same governments are also under pressure from the central government to report strong economic growth (a common authoritarian move, as we’ve previously discussed), they disregarded the ministry’s advice and instead “went on another borrowing spree.” Thus, by the end of last month, “the outstanding bonds of their financing vehicles ballooned to more than twice what it was in 2018.” Oops.
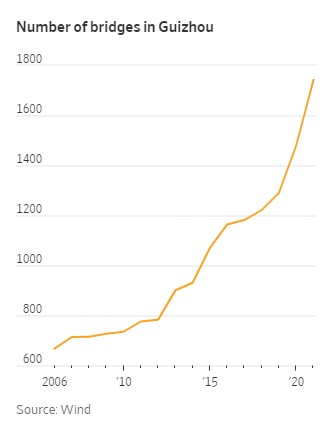
All this spending and debt raises several long-term economic concerns. For starters, the actual value of the local government projects at issue is increasingly in question—as is the past GDP growth it generated. Tales of useless and empty structures funded by Chinese government debt abound. “A high-speed rail station in Danzhou,” the WSJ reports, “cost $5.5 million to build but was never put into use because passenger demand was so low.” In debt-ridden Guizhou, meanwhile, a single state-owned company built 24 of the world’s 100 highest bridges (including the world’s highest) in the province, and “by the end of 2019, the total length of Guizhou’s highways was the fourth-longest in the country, topping some of the wealthier provinces like Guangdong and Zhejiang.” All that debt and construction contributed to Guizhou’s eye-popping 9.5 percent annual GDP growth from 2011-2022, but now the bill is coming due—and, as one Chinese credit analyst put it, “Eventually, someone must pay for it.”
That “someone” gets to the second debt problem: Analysts increasingly believe that China’s central government will have to step up and take on large amounts of new debt to pay for the provinces’ reckless spending (which Beijing, of course, encouraged). For this and related reasons, Moody’s Investors Service recently downgraded China’s credit rating to negative from stable, “because the country is likely to provide more support to financially stressed local governments and state-owned enterprises.” That’s not only a reputational black eye for the CCP but will also make borrowing more costly in the future.
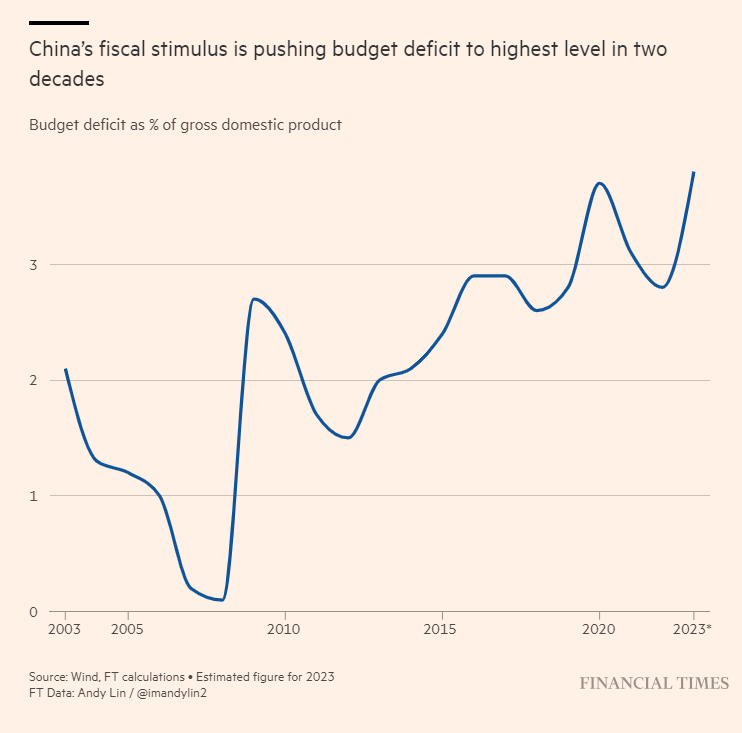
Third, all this debt and overinvestment could mute future government efforts to stimulate the economy via fiscal policy—even if Beijing technically has room on its (public) balance sheet to do so. From the WSJ:
“The leading point is they are running into diminishing returns in building stuff,” [Harvard economist Ken Rogoff] said, “There are limits to how far you can go with it.”
With so many needs met, economists estimate China now has to invest about $9 to produce each dollar of GDP growth, up from less than $5 a decade ago, and a little over $3 in the 1990s.
Returns on assets by private firms have declined to 3.9% from 9.3% five years ago, according to Bert Hofman, head of the National University of Singapore’s East Asian Institute. State companies’ returns have retreated to 2.8% from 4.3%.
This “pushing on a string” problem, combined with concerns about tepid tax revenues and off-book debts, has caused many analysts to “question just how much budgetary firepower Beijing really has to boost flagging confidence and drive stronger economic momentum”—even though China has stepped up spending in response to recent economic turmoil.
China’s much-vaunted manufacturing sector, meanwhile, may be suffering from similar problems. Chinese governments have subsidized numerous “strategic” sectors like steel, shipbuilding, and electric vehicles, but—thanks to lagging domestic and global demand and increasing geopolitical tensions (often caused by those same subsidies!)—they may have no place to sell it. As a result, the sector has teetered this year between mild expansion and (more often) contraction:
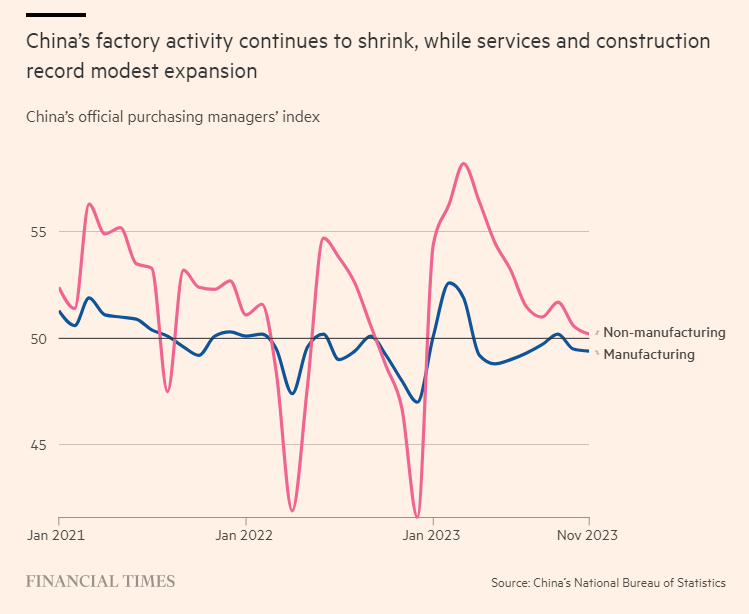
Meanwhile, non-manufacturing industries just hit “the lowest reading since China was swept by Covid last December.”
Outside the corporate sector, other problem signs have emerged. Most notably, the youth unemployment rate hit a record high of 21.3 percent in June … right before the government ceased to publish the official number. (Always a good sign!) Add students to the total, and the rate could be 46.5 percent. Shockingly, nixing the stat didn’t make the problem go away: As the WSJ’s Josh Zumbrun writes, social media reports and independent data show that youth unemployment remains a “troubling story” in China, even if we can’t pin down exactly how troubling it is. Meanwhile, one private forecaster’s “measure of job openings began to plunge in May, and as of early December was 35 percent lower than a year earlier—not a great sign in an economy desperately trying to absorb huge numbers of jobless youth.” Assuming the rate is still hovering around those June levels, it’d be one of the highest in the world:
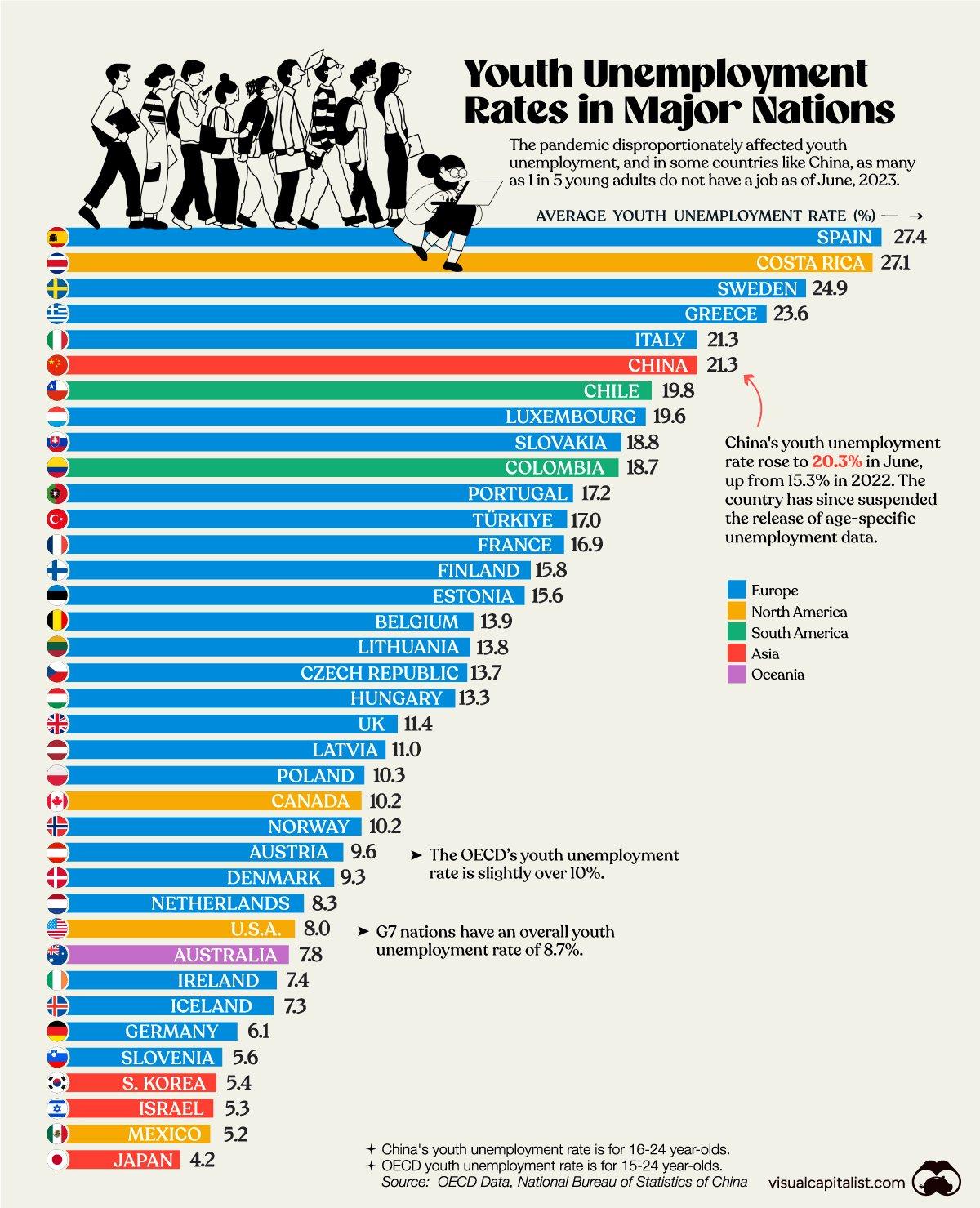
One of the issues here, the New York Times notes (along with many others), is a policy-driven mismatch between the types of young workers China’s planners once wanted its education system to produce (college grads to work in services or government) and the “strategic” industries the government is currently supporting (which need factory workers trained primarily at vocational schools). Thus, for example, “The number of teenagers entering vocational and technical high schools plummeted 25 percent between 2010 and 2021,” while “about 60 percent of the Chinese population turning 18 enroll at a university”—up from 10 percent in 2000. Now, China’s burgeoning EV industry faces “a shortfall of skilled technicians as young people shun manufacturing careers.”
Problems are not, however, isolated among China’s young. As the Peterson Institute’s Adam Posen documented in August, Chinese households seem to have lost confidence in the future of the Chinese economy and government. As a result, they are saving more—a lot more—and consuming less: Compared with 2015, bank deposits (as a share of GDP) are up by 50 percent and remain elevated, while consumption of durable goods has declined by about one-third. Private investment (down two-thirds since 2015) shows a similar insecurity.
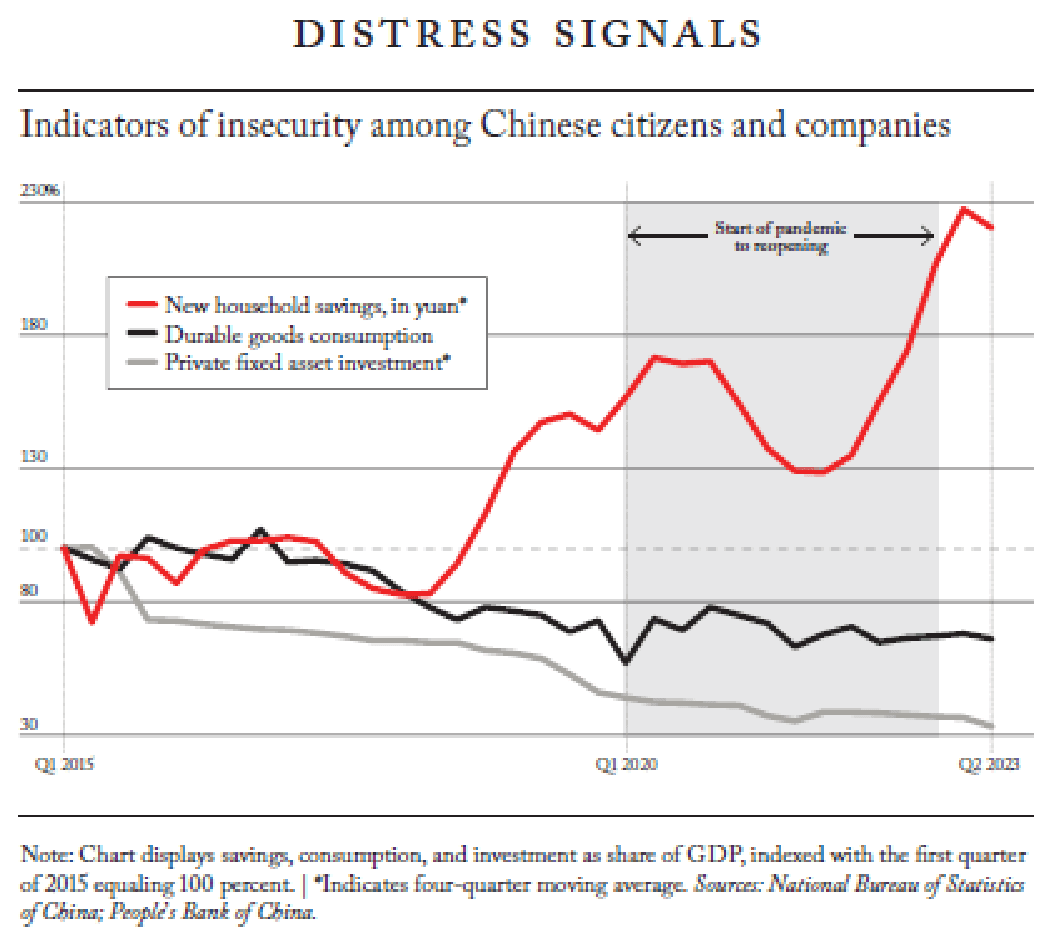
WSJ’s Nathanial Taplin came to a similar conclusion a couple weeks later after looking at a different set of consumer survey and loan data: “Beijing has failed to convince households that their financial future is secure in the post-Covid era.”
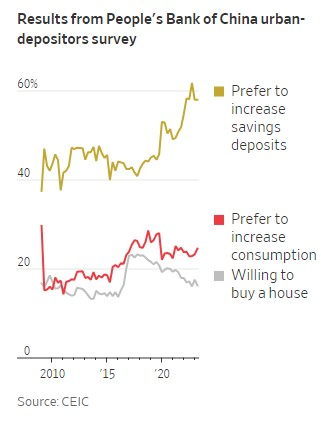
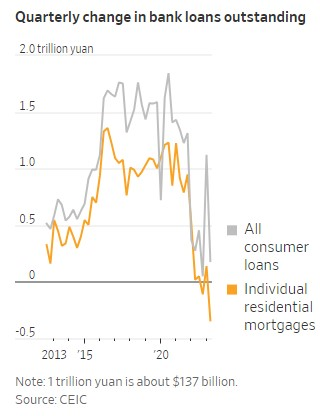
Unless the CCP focuses more on consumption and less on “grandiose industrial policy and geopolitics,” Taplin adds, a “painful period of economic stagnation” might be ahead. He and Posen are certainly not alone in their diagnoses and warnings.
Other signs of household stress have since emerged. Earlier this month, we learned that “defaults by Chinese borrowers have surged to a record high … highlighting the depth of the country’s economic downturn and the obstacles to a full recovery.” Making matters worse is Chinese law, which requires these 8.5 million people to be “officially blacklisted” and thus “blocked from a range of economic activities, including purchasing aeroplane tickets and making payments through mobile apps such as Alipay and WeChat Pay, representing a further drag on an economy plagued by a property sector slowdown and lagging consumer confidence.” Lower incomes and higher costs, meanwhile, have caused China’s massive state health insurance system to lose tens of millions of subscribers in 2022—an “unprecedented” decline that, after years of growth, is expected to continue this year.
Structural Headwinds and ‘Japanification’?
Other, longer-term headwinds also remain problematic, as I first documented here back in 2021 and as my Cato colleague Clark Packard recently updated in an essay for our ongoing globalization project. Along with debt, China’s demographics (low birth rates, a rapidly aging population, shrinking workforce, etc.), difficulty attracting and retaining both homegrown and global talent, and stagnating economic dynamism and productivity pose further challenges to future economic growth, government budgets, and political stability.
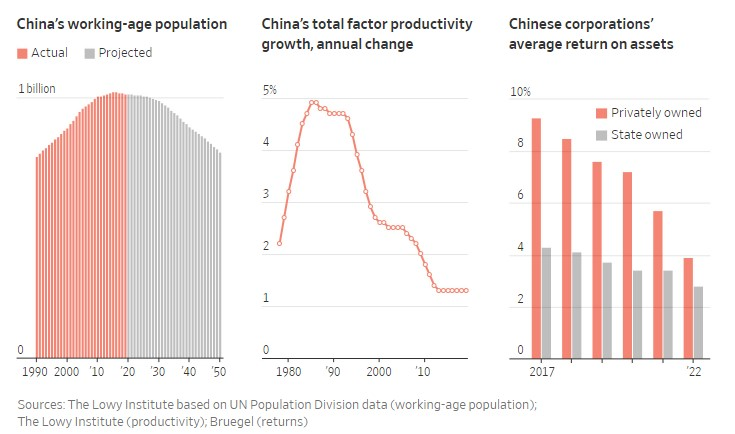
Combine these headwinds with the shorter-term issues, and the narrative around China has shifted radically in the last year. Analysts once attracted to (or worried about) strong growth are suddenly reversing course and worrying about excess capacity and stagnation. Unlike most other big economies, in fact, China is now grappling with deflation: Consumer prices went negative in July, returned there in October, and declined even more last month, indicating that a brief late-summer revival may have been a “dead-cat bounce.” Producer prices, meanwhile, have been negative for a full year.

Perhaps most troubling for the Chinese economy is the fact that these problems have arisen despite “a slew of supportive measures from Beijing to boost sentiment and growth since mid-2023.”
Pushing on a string, indeed.
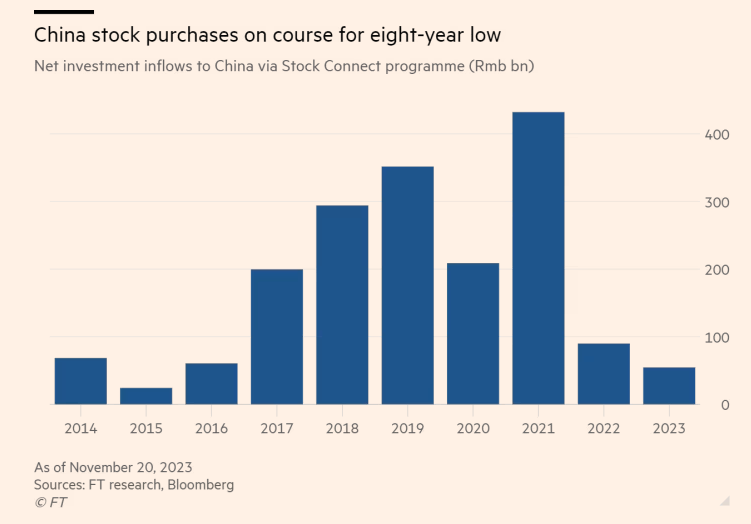
None of this means that China is on the verge of an all-out economic collapse or anything, but investors have significantly revised their bets on the Chinese economy. As of late November, “more than three-quarters of the foreign money that flowed into China’s stock market in the first seven months of the year has left, with global investors dumping more than $25bn worth of shares despite Beijing’s efforts to restore confidence.”
And foreign direct investment is fleeing China in ways not seen in decades—not just slowing their investments there but “now ditching Chinese investments and pulling money out at a remarkably rapid pace” for the first time ever.
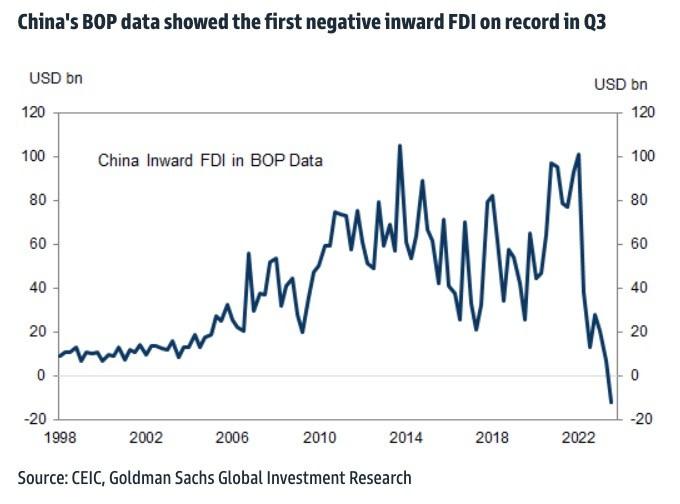
If these FDI trends continue for the rest of the year, the FT’s Robin Wigglesworth adds, “China is on track to attract less FDI than Poland did in 2022, and less than half of what Sweden did”—and, he notes, even that might be too optimistic.
As a result, many analysts who once confidently predicted China’s economy would soon overtake the United States’ have lowered their growth projections, extended their timelines, or even ditched them altogether. Now, commentators openly wonder if China will be the “next Japan,” meaning a rapidly growing economy once predicted to supplant the United States, but instead—thanks to high levels of debt and state-directed economic distortions combined with slower growth and demographic and external pressures—ends up facing not just a few months or even a year of economic malaise but decades:
Some economists see alarming parallels between China’s current predicament and the experience of Japan, which struggled for years with deflation and stagnant growth. In the 1990s, a collapse in stock markets and real-estate values in Japan pushed companies and households to drastically cut back spending to service burdensome debts—a so-called balance-sheet recession that some see taking shape in China today.
As one analyst recently put it this summer: “When the real estate bubble started collapsing last year, all these Chinese economists began to worry about a Japan-like situation where so many people are paying down debt all at the same time and [the] economy could then fall into a deflationary spiral. I think that is actually already happening in China.” The latest deflation data would appear to confirm his fears (at least for now).
Beyond the aforementioned debt and deflation similarities between the two nations, there are plenty of others: banking, property, demographics, a high-savings/investment economic growth model, and policy-driven malinvestment and overcapacity (especially in manufacturing and infrastructure). It’s not a stretch to think that China’s economic engine will be sputtering for years to come, much like Japan’s did decades ago.
In fact, China’s situation is in many ways worse than Japan’s was when it began to stall. For starters, China is still relatively poor:
China’s national income per person reached about $12,850 last year, below the current threshold of $13,845 that the World Bank classifies as the minimum for a “high-income” country. Japan’s per capita national income in 2022 was about $42,440, and the U.S.’s was about $76,400.
China’s economic imbalances are also bigger than Japan’s were in 1990, as are its total debts (that we know of!):
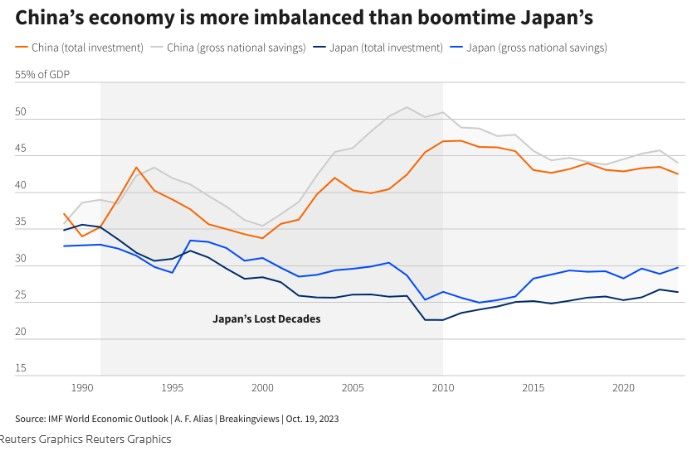
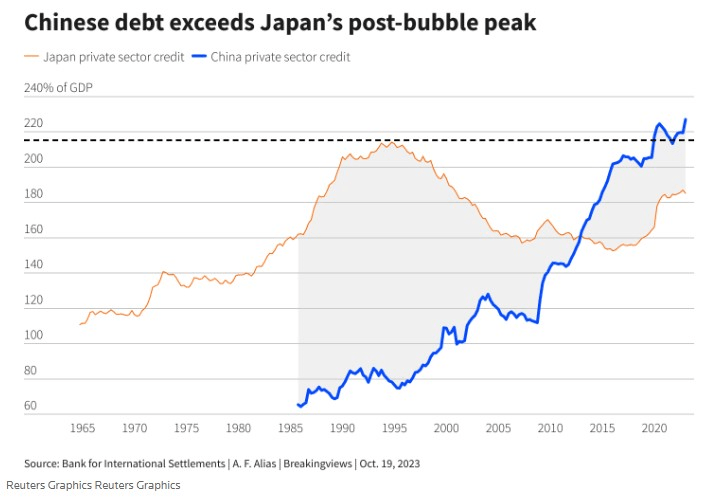
As Goldman-Sachs notes, China’s demographics headwinds also are bigger than Japan’s were in the 1990s, and its housing sector weakness is “more pronounced” too. Japan also didn’t pursue its own version of China’s wasteful and ineffective Belt & Road Initiative. And instead of backing off the economic meddling like Japan eventually did, China’s now leaning in:
Guided by a desire to strengthen political control, Xi’s leadership has doubled down on state intervention to make China an even bigger industrial power, strong in government-favored industries such as semiconductors, EVs and AI.
While foreign experts don’t doubt China can make headway in these areas, they alone aren’t enough to lift up the entire economy or create enough jobs for the millions of college graduates entering the workforce, economists say.
Just yesterday, in fact, China’s top central planners “vowed to make industrial policy their top economic priority next year,” thus letting down investors who were hoping the government would shift away from “technology self-reliance” toward more pro-growth policy instead.
Finally, there are the negatives raised by China’s political system, aside from the much-publicized corruption and institutional shortcomings (see chart below). As discussed last year, for example, authoritarian regimes have informational problems from both the bottom up (e.g., local governments distorting facts/data to avoid punishment) and the top down (e.g., the central government doing the same to make its regime look good). Autocratic systems also provide government officials with the mechanisms to forcibly restrict countervailing data (e.g., youth unemployment), which can distort government and private sector decision-making and discourage foreign investment. Posen adds that authoritarian regimes have a long history of starting out strong (fed by government largesse) but inevitably intervene in the economy in “increasingly arbitrary” ways—ways that boost uncertainty, cause households and businesses to hoard cash and avoid risk, and persistently slow economic growth. Once this cycle gets going, it’s difficult to reverse without fundamental reforms, none of which appear to be on China’s horizon.
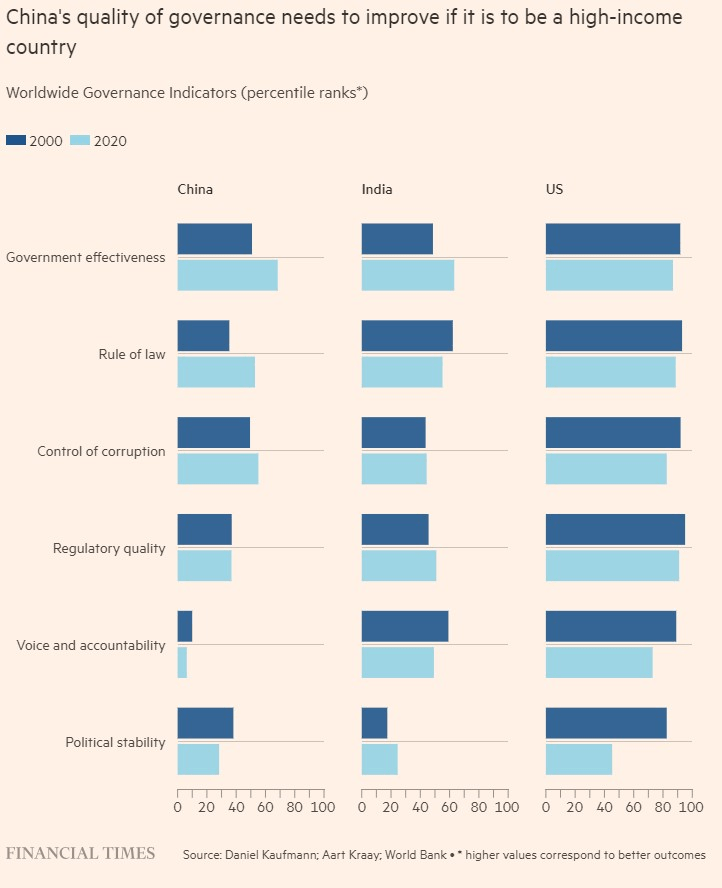
So, far from being fueling prosperity, Chinese state capitalism and autocracy could be an anchor in ways Japan never had to deal with.
Summing It All Up
Despite all the similarities and my own personal biases, I remain reluctant to embrace China’s “Japanification” narrative for numerous reasons. Most notably, China today fundamentally differs from 1990s Japan in ways—politics, foreign policy, level of government intervention in the economy, human rights issues, sheer size—that make this cross-country comparison even more difficult than such analogies usually are. And, it should be noted, many of the same analysts talking about “Japanification” are quick to follow with notes about how China might avoid Japan-style stagnation because its economy today is in some ways better off than Japan’s was in 1990, and because the Chinese government has more “policy space” to act. The precise direction of China’s future economy—lost decade, slower-but-steady growth, full-on collapse, or something else—remains unclear.
What is clear today, however, is that Xi Jinping’s China is not nearly the unstoppable economic powerhouse that many believed it to be—and wanted the United States to copy—just a short time ago. (See, for example, Cass, Atkinson, Prestowitz, Rubio, Dalio, and Kerry/Khanna to name just a few.) There again lies another parallel with Japan: as R Street’s Adam Thierer documented in 2021 (and as us geezers can recall firsthand), Japanese industrial policy and planning once caused many American wonks and policymakers to predict Japan’s inevitable economic dominance and to propose all sorts of U.S. subsidies and protectionism in response. People wrote books and made movies about the “Japan threat,” and implored Washington to copy Tokyo’s economic model:

That dominance, of course, never materialized. Indeed, just as those books were being published (written by some of the same folks screeching about China today, by the way), Japan was beginning its long period of economic stagnation, with the Japanese government years later admitting that its vaunted economic model was a big part of the problem.
China might not follow the exact same path as Japan, but it sure does seem to be heading in the same general direction. And as we discussed a few months back, there are already plenty of signs that China’s industrial policies aren’t nearly the big winners some have claimed. (More have since emerged, by the way.) One can be forgiven for missing the warning signs in that some of us saw years ago through the fog of positive Chinese economic data. Dire warnings today, however, deserve much less sympathy—and attention.
Hopefully Congress will give them what they deserve.
Chart(s) of the Week
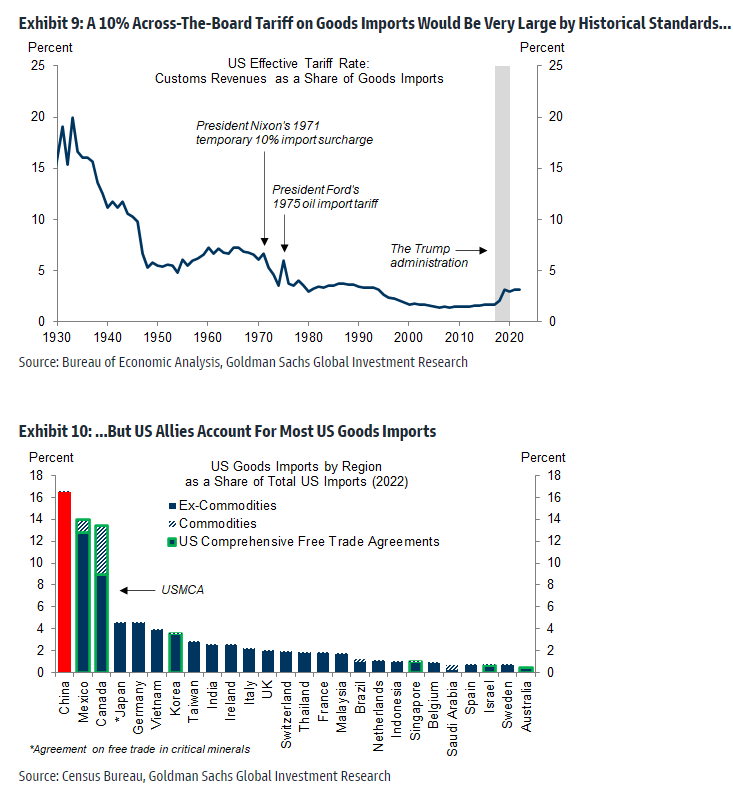
Trump wants historically large tariffs on (mainly) U.S. allies:
The Links
New Defending Globalization essays on “The China Shock” (by me) and global capital flows (by Norbert Michel)







Please note that we at The Dispatch hold ourselves, our work, and our commenters to a higher standard than other places on the internet. We welcome comments that foster genuine debate or discussion—including comments critical of us or our work—but responses that include ad hominem attacks on fellow Dispatch members or are intended to stoke fear and anger may be moderated.
With your membership, you only have the ability to comment on The Morning Dispatch articles. Consider upgrading to join the conversation everywhere.