There was a time when the biggest name in censorious pop-culture scolds was a Democrat: Tipper Gore, at the time Mrs. Al Gore, one of the “Washington Wives” behind the Parents Music Resource Center. PMRC is now known mainly as a retro-’80s Trivial Pursuit answer, but it was once emblematic of a certain kind of well-heeled evangelical hysteria and the force behind the effort to put warning labels on music and video games with sexual, violent, or otherwise objectionable themes.
You have to use a little bit of historical imagination here. In the 1980s, the Democratic Party did not count drag queens as a major constituency. Social conservatism was more or less the norm in Washington, and a bipartisan norm at that: Al Gore was, at the time, a pro-lifer, albeit a generally mild one, as had been a great many prominent and soon-to-be-prominent figures in the Democratic Party such as Bill Clinton (“I am opposed to abortion and to government funding of abortions”). See also: the Rev. Jesse Jackson (“It takes three to make a baby: a man, a woman and the Holy Spirit”), Gov. Robert Casey of Pennsylvania (infamously shut out of the 1992 convention lest he say something nonconforming on the issue), and Democratic Majority Leader Rep. Dick Gephardt (“I believe that the life of the unborn should be protected at all costs”), whose promise to remain “steadfast” on the issue lasted right up until he decided to run for president.*
Socially speaking, those were more conservative times. But much more relevant is the fact that those were extraordinarily paranoid times. (The conservatism and the paranoia do go together, at times, though not in the way our progressive friends suggest in their efforts to pathologize political disagreement.) My own theory is that the divorce boom of the late 1960s and 1970s left a great many fractured families in its wake, with parents—both the one doing the raising and the estranged one—having seen by the early 1980s that they had made a terrible mistake and done their children a terrible disservice, that these children being raised by single parents (single mothers, overwhelmingly) or in so-called blended families were going to be a troubled generation, suffering radically higher rates of physical, emotional, and sexual abuse than children raised in homes with two married parents. All that abuse and neglect was interacting with headlines screaming about elevated crime rates (the U.S. homicide rate hit a record in 1980, while New York City had 2,605 murders in 1990, compared to 386 in 2023), the explosion of crack cocaine use, etc. As is always the case in such times, there was one obvious imperative, one thing the American people needed above all else: someone to blame.
When you are looking for a scapegoat, you need a combination of things: They have to have enough cultural status and cachet to be credible as a villain, but they cannot have any real power, lest they fight back. You need someone who is easy to hate—or at least easy to mistrust—which makes members of racial, religious, political, and sexual minorities attractive candidates. You need someone or something recognizable, preferably instantly recognizable the way a celebrity or someone who wears distinctive religious garb is recognizable, and it doesn’t matter if it makes any sense. (After 9/11, a few angry Americans turned their rage on Sikhs, whose religion was founded in part as an escape from Islam, but one turban is evidently as good as another.) And so Tipper Gore et al. settled on musicians, especially rappers and heavy-metal performers.
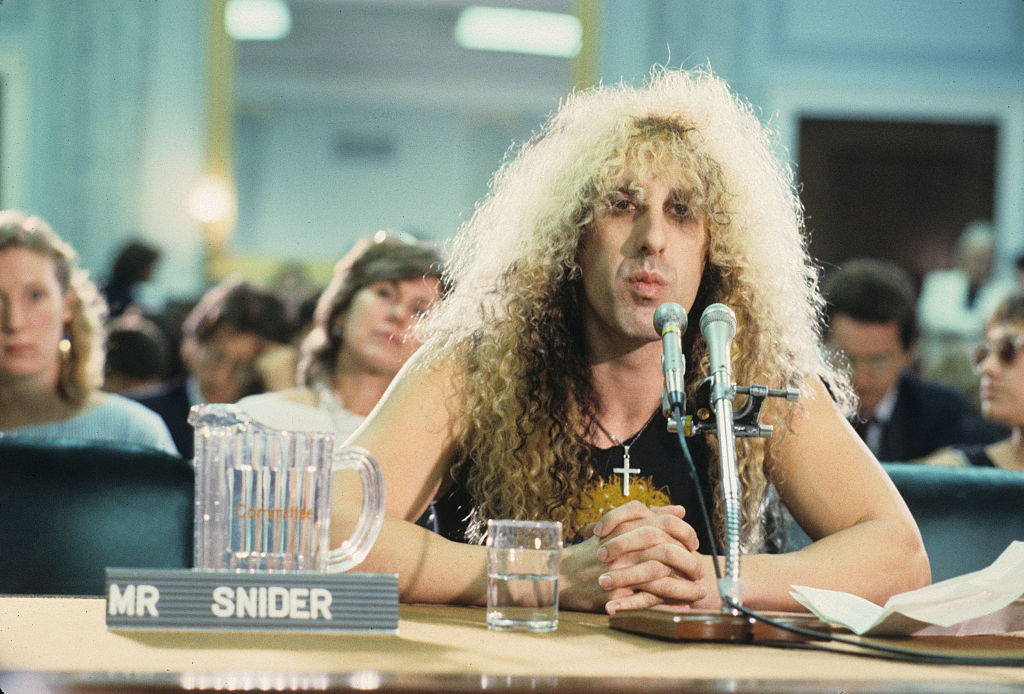
It was a matter of aesthetics, not one of morals. Dee Snider of Twisted Sister was a literal Christian choirboy (all-state chorus in high school, no less!) and doesn’t seem to have been much of a sexual deviant (he has been faithfully married to the same woman since 1981), but he sure looked like a class-A weirdo back in the day. Most of the infamous gangster rappers of the 1990s either exaggerated their criminal résumés or invented them outright, ingeniously repackaging white America’s racial paranoia to sell it back to them at a tidy profit; they were writers and actors of the stage, part of an ancient tradition, but, in spite of their fundamentally literary character, they were very useful stand-ins for the actual crime wave that was happening in American cities.
Black hoodlums and degenerate boys in lipstick and eye-shadow: Plus ça change, plus c’est la même chose.
(People often expect performers such as Ice-T to be real-life versions of the characters they invent and lambaste them when they move on to other things, as Ice-T did taking up his career as a television cop; but, as I have noted before, nobody gets bent out of shape when Anthony Hopkins doesn’t eat people. Nobody ever thought Mick Jagger was actually a street-fighting man—he was a middle-class kid from Dartford studying accounting at the London School of Economics when the Rolling Stones started to blow up. When Rob Halford of Judas Priest was dragged into court as part of a ridiculous trial about whether supposed subliminal messages in his songs had led a teenager to kill himself, people were shocked when the man who showed up in the courtroom was the real-life Rob Halford, a mild-mannered, articulate, balding Englishman in a natty suit, rather than the leather-daddy maniac he plays on stage, like he would just walk around in the sunlight festooned with ten-penny nails and a cast-iron codpiece or whatever it was he was wearing for shows back then. It’s a funny old world.)
It was a weird moment. America’s marital chaos came to a head as the divorce rate peaked in 1981, with Ronald Reagan newly installed in the White House (in spite of weirdly persistent rumors that he might be the Antichrist) and Moscow’s stooges declaring martial law in Poland and sending inconvenient trade unionists to internment camps. In 1983, nearly one-half of all U.S. households tuned into The Day After, a made-for-TV movie about nuclear war between the United States and the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, and, apparently, a fair number of viewers thought it was real. In autumn of that year, the Soviets shot down Korean Air Lines 007, a commercial flight from New York to Seoul via Anchorage, Pershing II missiles were deployed in what was still then known as West Germany, the United States went to DefCon 1 and narrowly avoided war with the Soviet Union when U.S. exercises were mistaken for an attack, and the Soviets angrily walked out of arms-control negotiations in Geneva.
When the big things feel like they have spun into chaos, it is tempting to try to really clamp down on some of the little things, as a way of giving yourself a false sense of being in control. (I knew a guy who quit smoking after being diagnosed with some terrible health problems that had nothing to do with smoking—he just needed to feel like something about his well-being was within his own powers.) That’s what we did with the warning labels on NWA albums in the Age of Tipper Gore: The chaos in our families had led to chaos on the streets (in that much, I am a Confucian), and the weakness of the United States in the 1970s had emboldened the idealistic socialists in the East—the worst mass murderers on the world scene since the Nazis were done in and arguably worse than them, if we’re talking sheer numbers—to act up from Afghanistan to Poland to Central America.
When I was in elementary school, once a month or so we were made to practice hiding under our desks in the event of a nuclear attack—an attack that, as one teacher laconically explained to a roomful of 8-year-olds, we surely would not survive, given our proximity to an Air Force base that trained bomber pilots and hence presumably was high on the Soviet hit list. (In much the same way that every third family in the South or Southwest is descended from a “Cherokee princess”—of which there is no such thing—in the Cold War, every other town was somewhere around No. 4 on the Soviet nuclear-strike list. People talked about their towns’ rankings as though they had firsthand knowledge of Kremlin war-planning. It was a thing.) At the end of the Carter years, we were subjected to gasoline rationing while in sight of the oil wells that were pumping crude out of the ground and sending it to be refined into gasoline. Inflation was out of control, and mortgage rates exceeded 16 percent by 1982. And then there was a kind of broad resurgence of conservatism that led to Reagan’s election in 1980, which, after a rocky start to his presidency, bloomed into a kind of conservative triumphalism. Maybe we couldn’t get the Russians out of Afghanistan, but we could exercise some control over … rap albums with a lot of shocking lyrics, or rock albums made by young suburban men with suspiciously androgynous hairdos.
And that was something. It didn’t lead to anything worthwhile, of course. Pop song lyrics today are a lot raunchier than they were in 1983, video games are as bad as they ever were, and we have a lot of 11-year-olds walking around with what amounts to the world’s entire supply of pornography in their pockets. Twisted Sister’s “We’re Not Gonna Take It” is, from the vantage point of anno Domini 2024, about as edgy as “The Way You Look Tonight.”
When we experience a lack of control—when we are buffeted about by forces that are many orders of magnitude more powerful than we are—we feel fear and anxiety, and, perhaps more important, we feel that our dignity has been injured. And injuries to dignity can be powerful motivators: What we call, for lack of a better word, globalization has made us wealthier and more free, providing us with both material resources and opportunities for enriching experiences that were reserved, if they were available at all, to the very rich and powerful only a generation ago. (Hence the once-evocative phrase “jet set,” words fused together by people who did not imagine Spirit Airlines and the deeply unglamorous experience of 21st-century air travel.) But globalization also exposes us to different kinds of risks and reveals interdependencies that we might not have comprehended otherwise, or might not have had. As the COVID-era supply chain disruptions illustrated so dramatically, we have all sorts of complicated dependencies on far-flung parties, many of whom are beyond the political control of our own government. Washington can huff and puff all day, but the orange juice situation in Brazil is going to be what it is going to be.
This is a very long way of getting around to Dr. Vivek Murthy, the U.S. surgeon general, who has a fairly dopey proposal for putting PMRC-style warning labels on social-media platforms. It’s a pretty simple thing he wants, a little advertisement reading: “Social media is associated with significant mental health harms for adolescents.” But, wait, say the experts. (Oh, the experts!) That “stretches and oversimplifies the scientific evidence,” according to the New York Times.
For many years, researchers have tried to determine whether the amount of time a child spent on social media contributed to poor mental health, and “the results have been really mixed, with probably the consensus being that no, it’s not related,” said Dr. Mitch Prinstein, the chief science officer at the American Psychological Association.
What seems to matter more, he said, is what they are doing when they are online — content about self-harm, for example, has been shown to increase self-harming behavior.
“It’s kind of like saying, ‘Is the number of calories that you eat good for you or bad for you?’” said Dr. Prinstein, who testified before the Senate on the subject last year. “It depends. Is it candy, or is it vegetables? If your child is spending all day on social media following The New York Times feed and talking about it with their friends, that’s probably fine, you know?”
(Oh, the American Psychological Association. “Psychology is pseudoscience” isn’t the hill I want to die on this week, but: Psychology is pseudoscience. Mostly.)
For students of catastrophist rhetoric, Dr. Murthy’s case will be entirely familiar.
One of the most important lessons I learned in medical school was that in an emergency, you don’t have the luxury to wait for perfect information. You assess the available facts, you use your best judgment, and you act quickly.
The mental health crisis among young people is an emergency—and social media has emerged as an important contributor. Adolescents who spend more than three hours a day on social media face double the risk of anxiety and depression symptoms, and the average daily use in this age group, as of the summer of 2023, was 4.8 hours.
Additionally, nearly half of adolescents say social media makes them feel worse about their bodies.
It is time to require a surgeon general’s warning label on social media platforms, stating that social media is associated with significant mental health harms for adolescents. A surgeon general’s warning label, which requires congressional action, would regularly remind parents and adolescents that social media has not been proved safe. Evidence from tobacco studies show that warning labels can increase awareness and change behavior. When asked if a warning from the surgeon general would prompt them to limit or monitor their children’s social media use, 76 percent of people in one recent survey of Latino parents said yes.[end block]
It’s always an emergency when you want to impose a policy without such tedious considerations as democratic accountability or piddly little questions like whether you have the legitimate authority in your current role to do the thing you want to do. Just declare the emergency, and then add in a chestnut like this one: “The moral test of any society is how well it protects its children.” Populists and anti-business progressives already are committed to the storyline that social media platforms such as Facebook will sink to any depth of corporate wickedness in the pursuit of profit, and you can see the rhetorical lines being drawn: Over here, “the children”; over there, mustache-twirling corporate villains.
But we have been here before. Warning labels on music and video games had no effect on public morals in the 1980s and 1990s, and warning labels on social media platforms are going to have no effect on the mental health of young people in our time.
There are other approaches that might work.
Dr. Murthy writes: “As a father of a 6- and a 7-year-old who have already asked about social media, I worry about how my wife and I will know when to let them have accounts.” Let me help here: The answer to “when?” is: never. Social media is a sewer, smartphones are the portal to that sewer, and you shouldn’t let your children have them. You can take $1,000 to a good used-book store and get enough reading material to keep your children busy until they are adults. That and a couple of subscriptions will do it. If your children whine about it, tell them “No,” tell them “No” again as necessary, and remind yourself who is the parent and who is the child and then act accordingly. Trying to make social media safe for children is like trying to make guns safe for children. I am as pro-gun a guy as you are going to meet, but they aren’t safe—being safe isn’t what they are made for. Social media is designed to give people instant, unmediated access to the very worst that humanity has to offer. That is what it is there for. If somebody has something thoughtful, well-considered, and worthwhile to say, something that is of long-term value, then he can write a book like a civilized human being would, or at least a newspaper column. Don’t go camping in the garbage dump and then complain that it is full of garbage.
The town dump doesn’t need a warning that says it is full of garbage—it’s a dump. That’s what it’s there for.
The lesson we need about social media comes from the 1980s, but it isn’t warning labels.
It’s “Just Say No.”
And Furthermore …
The Supreme Court’s recent Rahimi decision, about which I will have more to say shortly, was one of two recent Second Amendment cases that weren’t really about the Second Amendment. The bump-stock case (Garland v. Cargill) wasn’t even notionally a Second Amendment case; the bump-stock rule cooked up by the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives (ATF) was challenged under the Administrative Procedures Act on the grounds that the ATF was making law in a way that it is not entitled to do, that the question of what the law should be is a matter for the lawmakers, i.e., for Congress. The words “Second Amendment” do not appear in the majority opinion, and, as far as I can tell, the opinion gives no indication that Congress could not pass a law to prohibit bump stocks. Justice Samuel Alito, in his concurrence, is explicit on the issue: “Congress can amend the law—and perhaps would have done so already if the ATF had stuck with its earlier interpretation.”
The Rahimi case was notionally about the Second Amendment, but it really ought to be understood as being about due process rather than the right to keep and bear arms. The Rahimi case was outrageously, maliciously represented, i.e. as in Slate’s insistence that “SCOTUS Is Really Considering if Domestic Abusers Should Be Allowed Guns.” The Supreme Court was considering no such thing—the question of whether people convicted of disqualifying crimes of domestic violence are entitled by the Second Amendment to keep and bear arms was never at issue in the case. The defining fact of the case was that Zackey Rahimi had never been convicted of any crime of domestic violence—he had never even been charged with one, and instead had been stripped of his civil rights based on a civil process, one in which Rahimi had enjoyed neither the benefit of legal counsel nor a hearing of the case before a court. As is the case in civil matters, Rahimi was involved in a process with a much lower standard of evidence than exists in criminal trials. Zackey Rahimi is by all accounts a real lowlife, and he seems to have been involved in a half-dozen shootings. But we do not strip people of their constitutional rights because they are bad guys or because we suspect that they have committed crimes. Rahimi voluntarily entered into a restraining-order agreement, partly under duress from the threat of being made to pay the other party’s legal fees if he contested the issue and lost.
This might be easier to understand if you thought of a civil right other than the right to keep and bear arms. If Rahimi had been stripped of his First Amendment rights, or incarcerated, or forbidden to vote without a criminal conviction, some of our progressive friends would no doubt see the question in a different light. They just don’t think of the rights protected by the Second Amendment as real rights, as legitimate.
The best point of comparison, in my view, is the process by which people are declared mentally incompetent or are remanded to involuntary psychiatric commitment. That doesn’t happen without a hearing with counsel or without substantial procedural protections for the targeted party—and, more important, it does not produce a result that includes open-ended forfeiture of a person’s civil rights or the imposition of felony penalties for non-compliance with treatment. Unlike someone committed involuntarily to psychiatric care, Rahimi did not have his liberties curtailed for two weeks, after which he would have an opportunity to petition for the reinstatement of his rights—he lost his rights indefinitely with no ready way to recover them.
For those who think Justice Clarence Thomas’ dissent in Rahimi is outrageous, ask yourselves: Which other civil rights should Americans be liable to forfeit without having been convicted of a crime? I understand that “due process” means only the process that is due, but it seems to me that the Bill of Rights should be made of sterner stuff, and that its protections should not be set aside by means of such a flimsy process as Zackey Rahimi endured.
Words About Words
The Times above seems to be violating its own style guide in the matter of Mitch Prinstein, Ph.D.
Dr. should be used in all references for physicians, dentists and veterinarians whose practice is their primary current occupation, or who work in a closely related field, like medical writing, research or pharmaceutical manufacturing: Dr. Alex E. Baranek; Dr. Baranek; the doctor. (Those who practice only incidentally, or not at all, should be called Mr., Ms., Miss or Mrs.)
Anyone else with an earned doctorate, like a Ph.D. degree, may request the title, but only if it is germane to the holder’s primary current occupation (academic, for example, or laboratory research). Reporters should confirm the degree holder’s preference. For a Ph.D., the title should appear only in second and later references.
For much more on “doctor,” see Jay Nordlinger’s characteristically interesting and erudite writeup.
Economics for English Majors
You can’t move all the jobs to Florida. But you can move Floridians to where the jobs are!
“I feel the American dream here,” said Alan Rodriguez, who moved to Warroad [Minn.] in October from West Palm Beach, where he was working at a window company that Marvin acquired in 2019. When orders slowed at that factory, Marvin asked for volunteers to come to Warroad temporarily, offering a $1,250 bonus. Rodriguez, 37, and his wife raised their hands and came for three weeks in June 2023.
Soon after arriving, Rodriguez, who moved to the U.S. from Cuba after winning a visa lottery in 2016, told his supervisor he wanted to stay. He and his wife were the first residents in the Icon Apartments, a new housing development in which Marvin is an investor. The company also supplied the windows and doors for the apartments, some of which are reserved for Path North participants and other Marvin employees. Rodriguez now earns $21 an hour as an assembler, up from the $16 he was making in Florida.
In my writing about Eastern Kentucky, a local told me sadly that some big company could build a factory in his poverty-stricken community, but it wouldn’t change things for the locals, because the company would have to import all the workers, given the state of the local labor offerings. Sometimes, people go where the work is—and, sometimes, work goes to where the workers are. U.S. workers have the advantage of being extraordinarily productive by world standards, and being productive is better than being cheap. An American worker who creates $5 in value for every $3 in wages is a better investment than a Pakistani worker who creates $3.40 in value for every $3 in wages—even if the American worker is paid 60 times as much.
Why aren’t the world’s manufacturers pouring into Haiti or Venezuela? Because the big corporations can’t afford that cheap labor.
Elsewhere …
A political profile followed by a little bit of meta-commentary on writing political profiles.
You can buy my most recent book, Big White Ghetto, here.
You can buy my other books here.
You can see my New York Post columns here.
Please subscribe to The Dispatch if you haven’t.
You can check out “How the World Works,” a series of interviews on work I’m doing for the Competitive Enterprise Institute, here.
In Conclusion
As mentioned above, last week I found myself a little bit annoyed with a Republican nobody down in Florida and kind of nuked him from orbit. Rhetorically, it was a fun exercise—the unexpurgated version was a lot more fun!—but there is a serious point, too. The Republican Party is never going to be a normal political party until it reckons with Donald Trump’s attempted coup d’état, which was not limited to the photogenic events of January 6, 2021. The Republican Party will not be able to move forward until people running for the House or for governorships can answer basic, obvious questions, such as: Who won the 2020 presidential election?
Evangelical Christians in particular are doing themselves no favors by associating themselves with an enterprise that currently requires bearing false witness. If you can’t even answer basic questions of fact—like whether Donald Trump dishonored himself and his family with Stormy Daniels in that Tahoe hotel room, irrespective of the question of whether he should have been charged with a crime in the ensuing hush-money controversy—then you are not going to be able to deal credibly with heavier issues: China, entitlements, debt, etc. I know that Republicans probably don’t feel this way, but I’m actually doing them a favor by not letting this stuff go.
You’re welcome, you dumb SOBs.
Correction, June 24, 2024: Due to an editing error, a quote in this paragraph was erroneously attributed to Bill Clinton rather than Dick Gephardt.









Please note that we at The Dispatch hold ourselves, our work, and our commenters to a higher standard than other places on the internet. We welcome comments that foster genuine debate or discussion—including comments critical of us or our work—but responses that include ad hominem attacks on fellow Dispatch members or are intended to stoke fear and anger may be moderated.
With your membership, you only have the ability to comment on The Morning Dispatch articles. Consider upgrading to join the conversation everywhere.